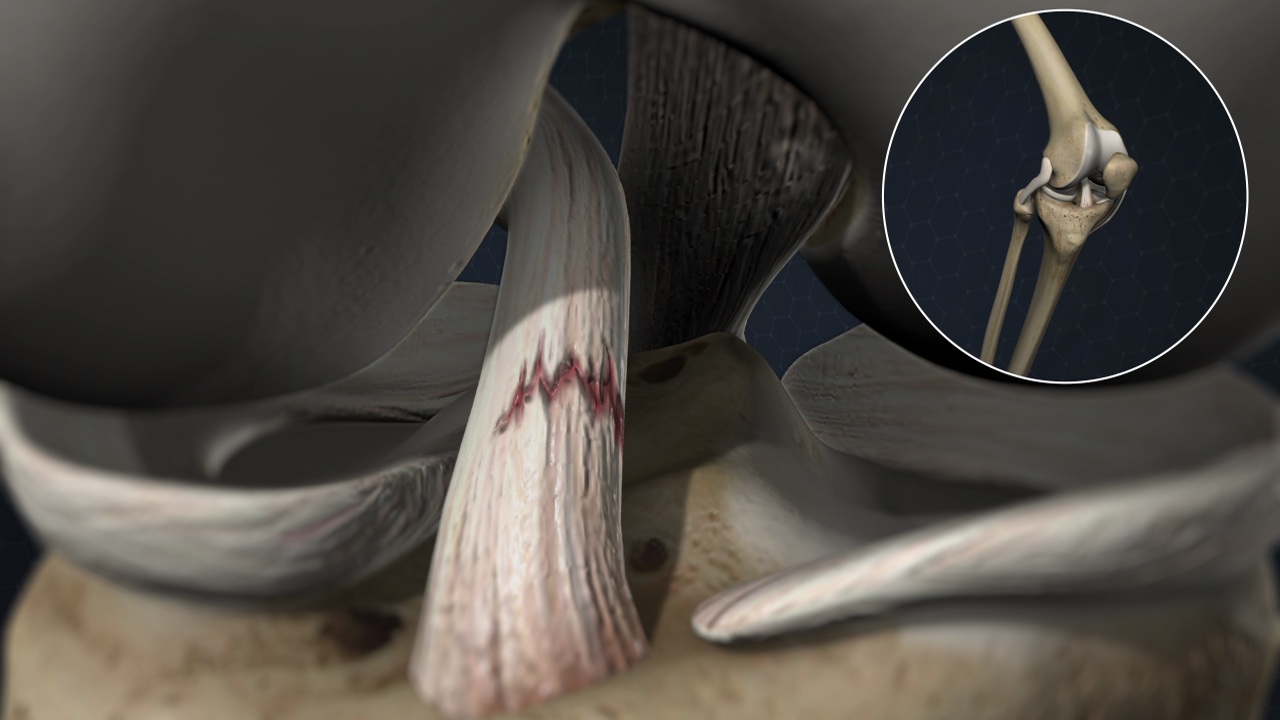
What is the anterior cruciate ligament?
The knee is a pivot joint kept intact by four ligaments. A ligament is a construction in the knee that keeps the bones intact and assists with controlling joint development or movement. There is a ligament on each side of the knee (the security ligaments) and two ligaments somewhere inside the knee. The two ligaments inside the knee that “cross” each other are known as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the back cruciate ligament (PCL). The two ligaments append on one side to the furthest limit of the thighbone (femur) and on the other to the highest point of the shinbone (tibia).
During action, the ACL controls how far forward the tibia can “slide” comparative with the femur: it basically acts to forestall a lot positive headway. While some level of movement or sliding is typical and is expected for knee capability, an excessive amount of movement might harm different designs in the knee which can prompt long haul issues in certain patients.
How is the ACL injured? What are the symptoms?
The ACL can be injured or torn in various different ways. The most well-known system is that of an unexpected turning or cutting move during wearing action, which is usually found in football, b-ball and soccer. The ligament can likewise tear because of work injuries or car crashes.
At the hour of the injury, a “pop” or “snap” can once in a while be felt or heard. How much torment experienced at the hour of the injury is somewhat factor yet can be very extreme. Regularly, the individual can’t proceed with play or action, and has the feeling that a critical injury has happened. Prompt enlarging of the knee creates at the hour of injury — inside the initial a few hours — however the extent of expanding can be restricted in the event that the knee is quickly chilled or supported.
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury or tear?
A “pop” in the knee at the hour of injury
Expanding of the knee
Failure to bear weight on leg (however some have next to zero agony)
Shakiness of the knee
How is an ACL injury diagnosed?
An ACL tear can be diagnosed by a doctor through a set of experiences and actual examination. On actual examination, the doctor can explicitly survey how much movement present and decide whether the ACL is torn. Moreover, assessment of different designs inside the knee is done likewise, as ACL tears are much of the time tracked down in relationship with injury to different designs inside the knee, like the ligament and security ligaments.
X-rays are taken to assess for the presence of any breaks. In numerous patients, a MRI output of the knee might be requested. The sweep can explain the topic of an ACL tear on the off chance that the set of experiences and examination are uncertain. The sweep is likewise valuable for assessing the ligament or meniscus tissue in the knee on the off chance that this data is important to go with choices in regards to the best treatment for a particular patient.
What are the different types of ACL injury or tears?
ACL injuries are generally grouped in grades of 1, 2 or 3.
Grade 1
Grade 1 injuries incorporate ACLs that have experienced gentle harm, e.g., the ACL is somewhat extended yet gives sufficient dependability to the knee joint.
Grade 2
Grade 2 ACL injuries are intriguing and depict an ACL that is extended and to some degree torn.
Grade 3
Grade 3 ACL tears happen when the ACL is torn totally into equal parts and is done giving any strength to the knee joint.
Tibial Spine Avulsion ACL Injury
Youths may likewise usually have what is known as a tibial spine avulsion ACL injury. With this sort of injury, the ACL itself isn’t torn, yet the hard connection of the ligament to the tibia (lower legbone) is pulled off. Contingent upon how far the hard connection of the ligament is pulled off, the injury can bring about shortcoming or precariousness of the knee on the off chance that it isn’t fixed.
What is the treatment for an ACL injury or tear?
Treatment choices depend on the patient’s symptoms, examination, the development staying in their development plates, sort of injury to the ligament, and the kind of sports and action objectives.
Nonsurgical
Nonsurgical treatment is generally suitable for grade 1 injuries. This would incorporate immobilization or propping, non-intrusive treatment, and a steady movement back to customary exercises and sports.
Surgical
Surgical treatment is suggested for people with a grade 3 or complete ACL tear. Surgical choices might change in view of the sort of ACL injury, whether the patient has open or shut development plates, and the sort.
What are the special considerations for a pediatric ACL injury or tear?
Youngsters and teenagers might have open development plates and a lot of developing left to do. This is a significant component and part of the conversation while gauging the choices for ACL treatment.
Assuming the patient has huge development staying, the treatment suggested will try not to upset the development plates so future development isn’t impeded.
Relevant Content Search:
physio for sports injuries |
do babies have acls |
pediatric acl repair |
long-term effects of acl tear without surgery |
some injuries can only be corrected surgically. |
acl xray |
sports injuries |
most common sports injuries |
explain what distinguishes acute and chronic sports injuries. |
sports injuries doctors |
what is the first step of the stop procedure for assessing acute sports injuries? |
sports injuries doctor |
worst sports injuries |
sports injuries treatment |
common sports injuries |
top 10 most common sports injuries |
explain what distinguishes acute and chronic sports injuries |
sports injuries examples |
how to prevent sports injuries |
youth sports injuries statistics |
recent sports injuries |
what is the first step of the stop procedure for assessing acute sports injuries |
of all body joints, what joint is most susceptible to sports injuries? |
youth sports injuries |
pediatric sports injuries |
which of the following statements about sports injuries is true? |